Researchers discovered compost and biochar could enhance carbon capture potential
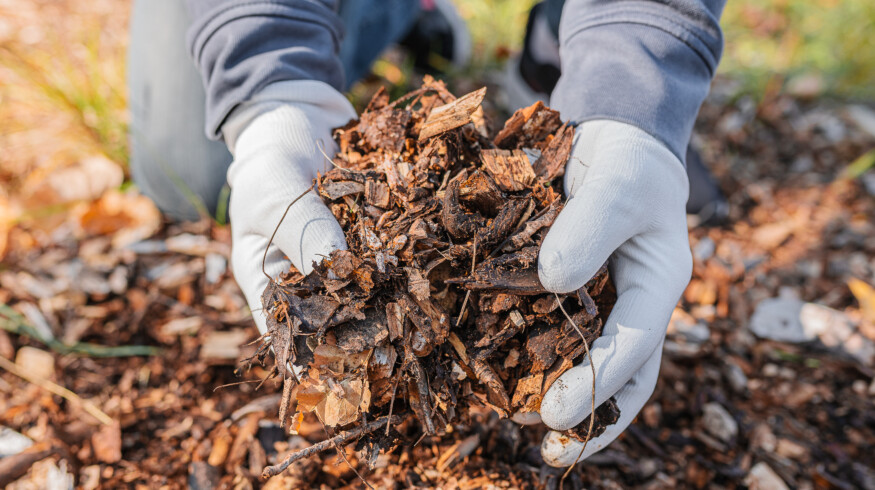

A three-year field study in California indicates that combining crushed silicate rock with organic amendments such as compost and biochar significantly improves the carbon sequestration potential of enhanced rock weathering (ERW), a method proposed for reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
The research, led by Tyler Anthony and published in AGU Advances, involved the application of crushed metabasaltic rock across grassland plots in Browns Valley, California. Some plots also received compost or a combination of compost and biochar—produced from locally sourced pine and fir residues. Control plots and compost-only plots were used for comparison.
While plots treated with crushed rock alone showed limited carbon uptake, they reduced organic carbon losses relative to untreated soil. In contrast, combining crushed rock with compost and biochar yielded stronger results, enhancing overall carbon sequestration and improving greenhouse gas mitigation. This mixture also helped reduce nitrous oxide emissions and promoted methane conversion.
The study estimates that applying this three-part amendment across 8% of California’s rangelands could sequester up to 51.7 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent annually. However, this represents only a fraction of the theoretical sequestration capacity for ERW in the region. The authors note that the study occurred during a period of drought, which may have limited the effectiveness of the treatments. They also stress the importance of accounting for emissions associated with material production, transport, and application when evaluating ERW’s net climate benefit.
The findings highlight the potential of supplementing ERW with organic inputs to enhance its effectiveness as a carbon management strategy, while also pointing to the need for comprehensive life-cycle assessments.
Enjoyed this story?
Every Monday, our subscribers get their hands on a digest of the most trending agriculture news. You can join them too!







Discussion0 comments